Hard Chrome Electroplating
Hard chrome electroplating is a process that involves depositing a layer of chromium onto a metal substrate to improve its hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. There are two types of chromium used in this process, hexavalent chrome and trivalent chrome. In this blog, we will discuss hard chrome electroplating and the differences between hexavalent and trivalent chrome.
Hard Chrome Electroplating
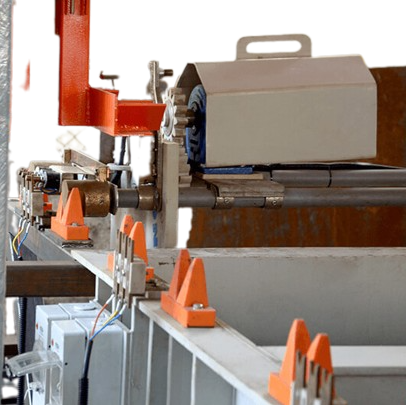
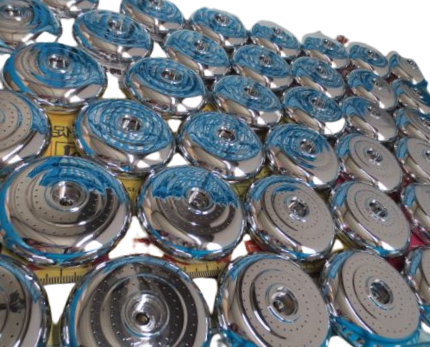
Hard chrome electroplating is a widely used industrial process that involves the deposition of a layer of chromium onto a metal substrate through an electrolyte solution containing chromium ions and sulphuric acid. The process is carried out through the use of an electrical current, which causes the chromium ions to be deposited onto the substrate.
The main advantage of hard chrome electroplating is its exceptional hardness and wear resistance. The plating provides a layer of protection against wear and abrasion, making it ideal for use in applications where parts are subject to high stress and wear. Another advantage is its excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for use in harsh environments where corrosion is a concern.
Factors that can affect the quality of hard chrome electroplating include the composition of the electrolyte solution, the current density, the temperature of the solution, and the surface preparation of the substrate. Proper control of these factors is essential to ensure consistent, high-quality plating.
Hexavalent Chrome
Hexavalent chrome, also known as hex chrome, is the traditional form of chrome electroplating. It is a highly toxic material that can cause serious health problems if not handled properly. However, it has exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for use in industrial applications.
Hex chrome is known to cause lung cancer, kidney damage, and other serious health problems. As a result, it is tightly regulated by government agencies and is subject to strict handling and disposal guidelines.
Trivalent Chrome
Trivalent chrome, also known as tri chrome, is a newer form of chrome electroplating that is much less toxic than hexavalent chrome. It also produces fewer harmful byproducts, making it more environmentally friendly. Trivalent chrome has good hardness and corrosion resistance, as well as improved adhesion and better dyeability compared to hexavalent chrome.
Trivalent chrome is considered safer to handle and dispose of than hexavalent chrome. It is also gaining popularity in the automotive industry, where it is used in place of hexavalent chrome for exterior trim parts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hard chrome electroplating is a widely used industrial process that provides exceptional hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance to metal substrates. Hexavalent chrome is the traditional form of chrome electroplating that has exceptional hardness and corrosion resistance but is highly toxic. Trivalent chrome is a newer, safer alternative that provides good hardness and corrosion resistance and is gaining popularity in the industry. Both hexavalent and trivalent chrome electroplating have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between the two ultimately depends on the specific application and regulatory requirements.